Crock Pot Cooking Time Chart – Food preparation is both an art and a science, and understanding the right cooking times can make all the distinction between a tasty dish and a cooking calamity. Whether you’re a skilled chef or a home cook, having a reliable food preparation time graph at your disposal is vital. In this post, we’ll dive deep right into the globe of cooking times, breaking down everything you need to know to ensure your meals turn out completely each time. Crock Pot Cooking Time Chart.
Relevance of Knowing Cooking Times
Food preparation times are vital for guaranteeing that your food is cooked extensively and securely. Proper cooking not just enhances the taste and structure of your recipes yet likewise aids stop foodborne illnesses. Overcooking or undercooking can considerably affect the high quality of your dish, making understanding food preparation times a vital skill in the kitchen.
Just How Cooking Times Affect Food Quality
Cooking times can influence more than just security; they likewise affect taste and structure. For instance, overcooked meat can come to be challenging and completely dry, while undercooked chicken can be dangerous to consume. A cooking time chart helps you strike the ideal equilibrium, ensuring your dishes are both safe and delicious.
Comprehending Food Preparation Times
What are Cooking Times?
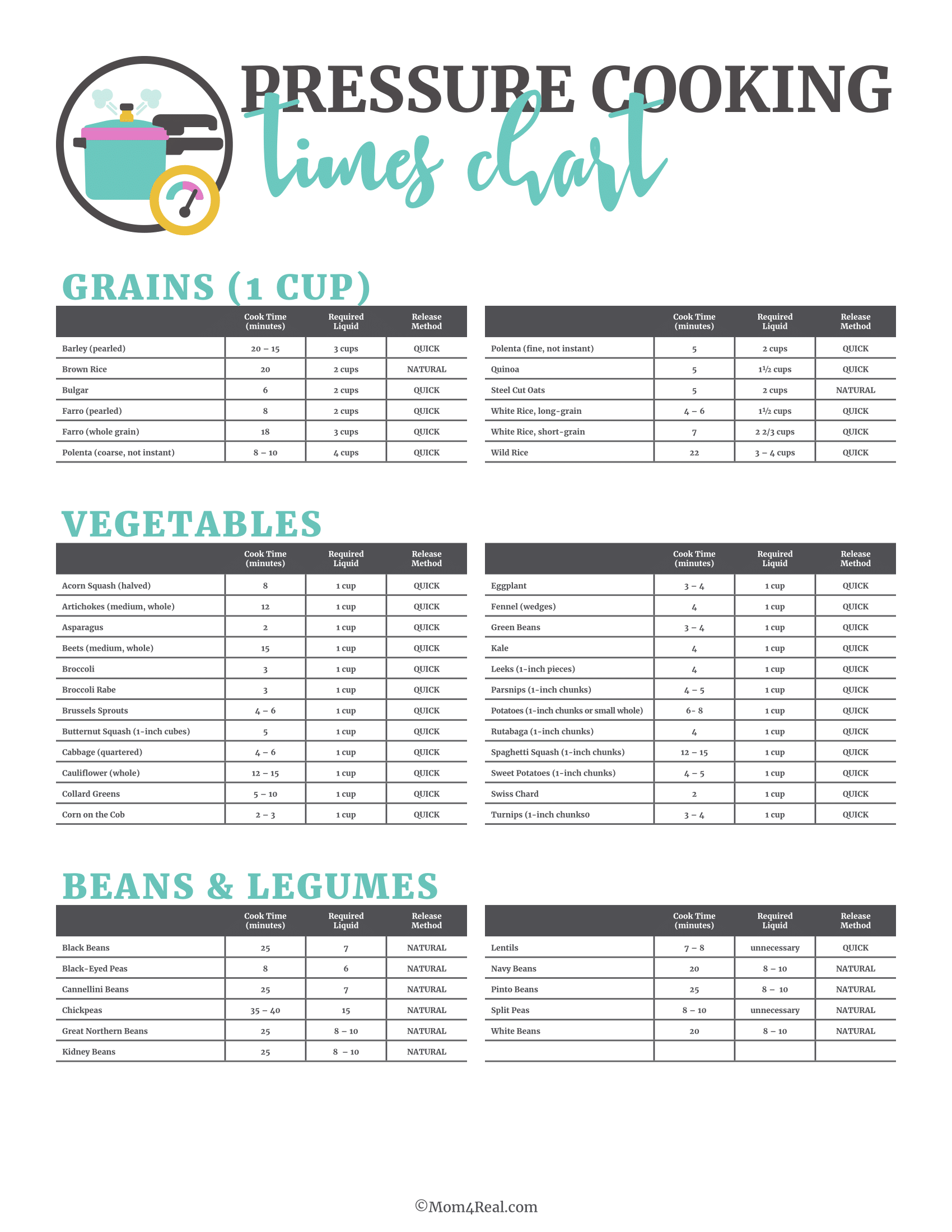
Food preparation times refer to the period required to prepare food to the wanted doneness level. These times can differ based upon the kind of food, its dimension, and the cooking approach used. A well-structured cooking time graph provides a fast reference for these times, making dish prep much more reliable.
Aspects Affecting Cooking Times
Several factors can influence cooking times, including:
- Size and Thickness: Larger or thicker items of food generally need more time to cook.
- Cooking Method: Different methods (e.g., baking, barbecuing) can influence just how promptly food cooks.
- Temperature level: Cooking at greater or lower temperature levels will transform cooking times.
- Altitude: Cooking times can be longer at higher altitudes because of reduced air pressure.
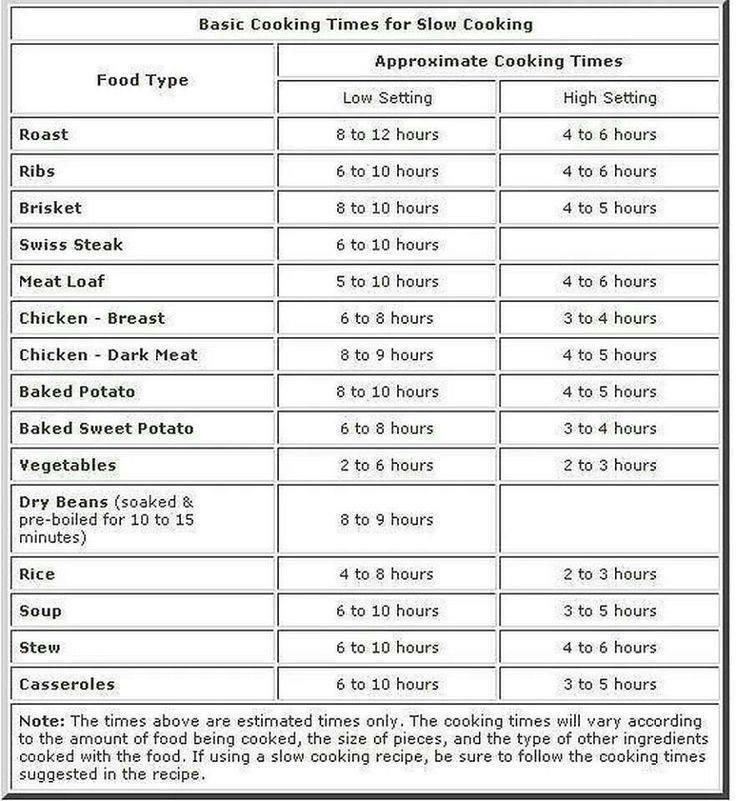
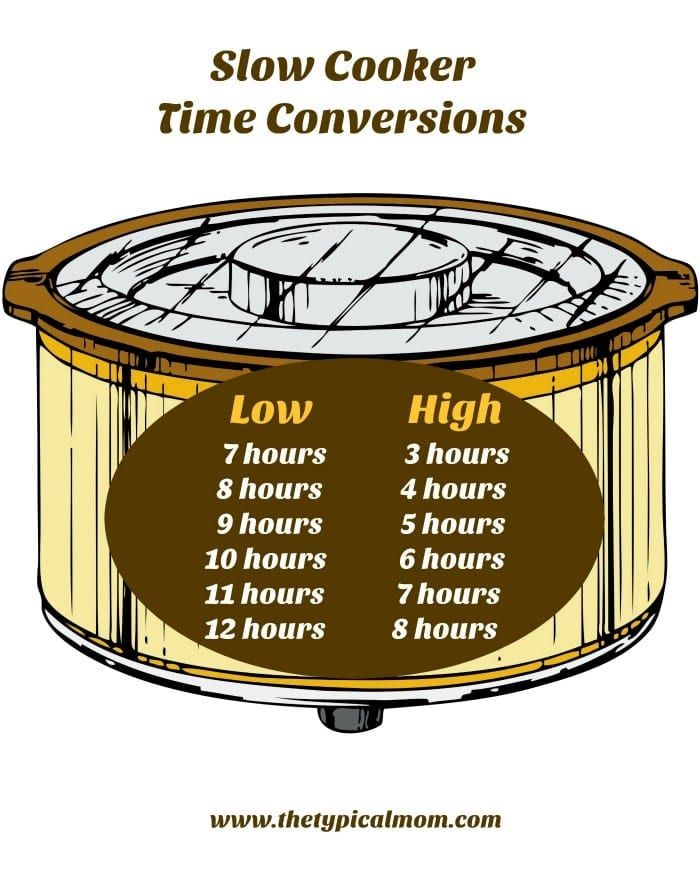
Cooking Time Graph Basics
Sorts Of Cooking Time Charts
Food preparation time charts can be classified into a number of kinds:
- General Charts: Provide typical cooking times for different foods.
- Specialized Charts: Focus on specific groups like meats or vegetables.
- Method-Specific Charts: Detail times based on food preparation techniques like cooking or grilling.
How to Utilize a Food Preparation Time Graph
Using a cooking time chart is easy. Find the sort of food and its prep work technique, after that refer to the recommended time. Change based upon your certain problems, such as oven type or food dimension.
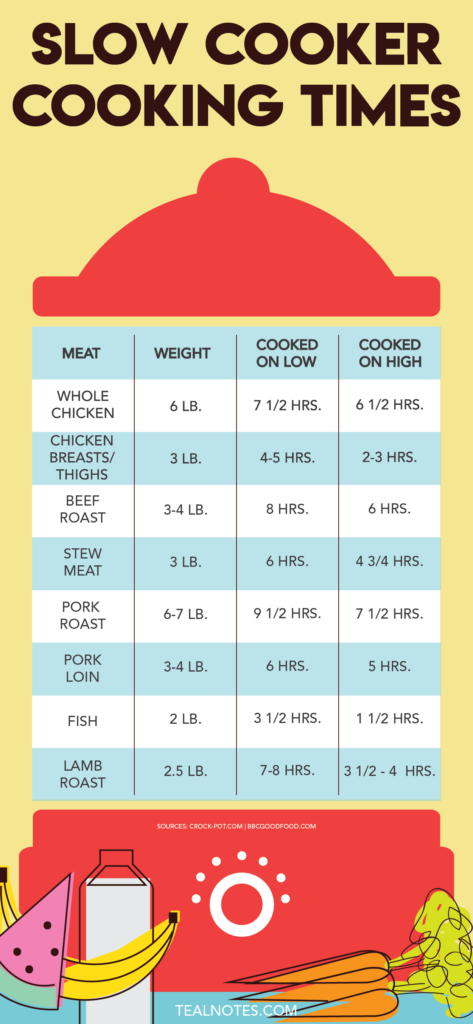
Meat Cooking Times
Beef
- Roasts: For a medium-rare roast, cook at 325 ° F( 163 ° C) for about 20 minutes per pound.
- Steaks: Grill or pan-fry for about 4-5 minutes per side for medium-rare.
Pork
- Roasts: Prepare at 325 ° F( 163 ° C) for 25 mins per extra pound.
- Chops: Grill or pan-fry for 6-8 mins per side, depending upon thickness.
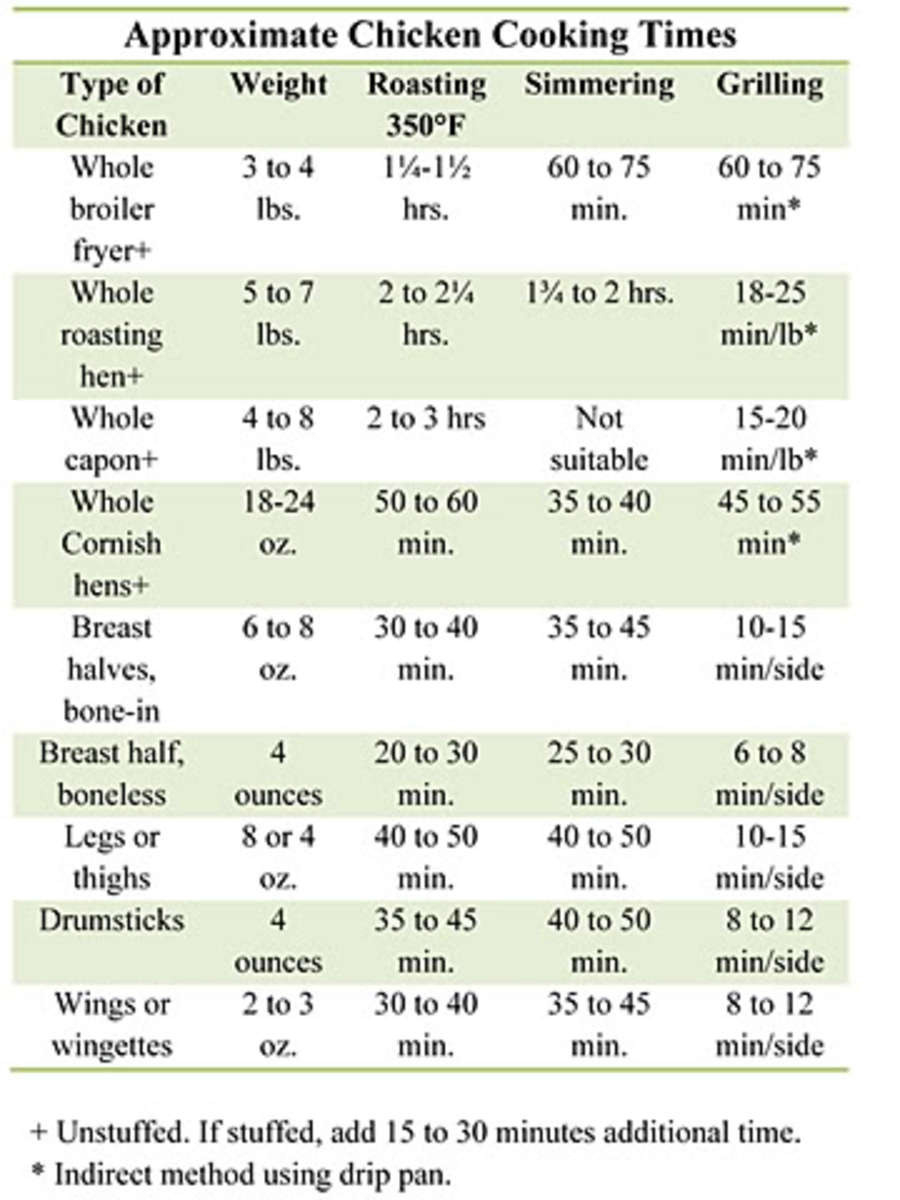
Hen
- Whole Hen: Roast at 350 ° F( 177 ° C )for around 20 minutes per pound.
- Poultry Breasts: Bake at 375 ° F( 190 ° C) for 25-30 mins.
Lamb
- Roasts: Cook at 325 ° F( 163 ° C )for around 25 mins per pound for medium-rare.
- Chops: Grill or pan-fry for 4-5 mins per side.
Fish And Shellfish Food Preparation Times
Fish
- Entire Fish: Bake at 400 ° F( 204 ° C) for 20 mins per
- extra pound. Fillets: Prepare at 375 ° F( 190 ° C )for 15-20 minutes.
Shellfish
- Shrimp: Boil or sauté for 3-4 mins until pink and opaque.
- Lobster: Steam for about 7-10 mins per pound.
Veggie Food Preparation Times
OriginVegetables
- Potatoes: Bake at 400 ° F( 204 ° C )for 45-60 minutes, depending on size.
- Carrots: Boil for 5-7 minutes or roast for 25-30 minutes.
Leafy Greens
- Spinach: Sauté for 2-3 minutes till wilted.
- Kale: Sauté or cook for 10-15 mins.
Cruciferous Vegetables
- Broccoli: Steam for 5-7 minutes.
- Cauliflower: Roast at 425 ° F( 218 ° C )for 20-25 minutes.
Cooking Times for Different Approaches
- Baking: Cooking times differ based on the recipe. Cakes, casseroles, and bread each have one-of-a-kind times and temperatures.
- Boiling: Boiling times depend upon the food. For pasta, it’s usually 8-12 mins; for eggs, about 10 mins for hard-boiled.
- Steaming: Steaming keeps nutrients much better. Veggies generally take 5-10 minutes, relying on dimension.
- Sautéing: Sautéing fasts, normally taking 5-10 mins for vegetables and 3-4 minutes for healthy proteins.
- Grilling: Grilling times vary widely. For meats, it can range from 4 mins per side for thin cuts to 20 mins per side for thicker pieces.
Unique Considerations
Elevation and Food Preparation Times
1. Recognizing Altitude Results
At higher altitudes, the lower atmospheric pressure can affect cooking times and temperature levels. For instance, water boils at a lower temperature, which suggests that cooking procedures may need more time to finish. Changing your dishes for elevation can make sure much better results.
2. Changing Food Preparation Times
- As much as 3,000 Feet: Slight adjustments are generally sufficient. Boost cooking time by concerning 5-10% or include a few extra minutes.
- 3,000 to 6,000 Feet: Modest changes might be needed. Increase cooking time by 10-20%, and sometimes enhance the temperature by 25 ° F to guarantee appropriate food preparation.
- Above 6,000 Feet: Considerable changes are required. Rise cooking time by 20-30% and readjust temperature setups as needed. For cooking, you could also need to adjust the amount of liquid and leavening agents.
3. Cooking at High Altitudes
Baking can be especially challenging. For cakes and cookies:
- Reduce Cooking Powder/Soda: Way too much can create rapid climbing and collapse.
- Rise Flour: To compensate for the lower thickness of air.
- Boost Fluid: To counteract the quicker evaporation prices.
Stove Variations
1. Oven Temperature Level Accuracy
Not all ovens warm evenly. A typical stove could have temperature variants of up to 50 ° F. This discrepancy can affect food preparation and cooking outcomes.
2. Testing Oven Temperature Level
To guarantee your stove is at the correct temperature level:
- Make Use Of an Oven Thermostat: Position it in the center of the oven and compare the reading to your oven’s temperature level setting.
- Normal Calibration: Calibrate your oven occasionally to maintain precision.
3. Checking Food Preparation Times
- Inspect Early: Start checking your food a few minutes before the suggested cooking time to stay clear of overcooking.
- Adjusting Dishes: If you locate your stove chefs quicker or slower, change your recipes as necessary by either minimizing or boosting cooking times.
4. Convection Ovens
Stove flow air, which can bring about quicker and a lot more also cooking. Typically, decrease cooking time by about 25% or lower the temperature by 25 ° F contrasted to conventional stoves.
Tips for Accurate Food Preparation Times
Making Use Of a Meat Thermostat
1. Significance of a Meat Thermostat
A meat thermometer is an crucial device for ensuring that meats get to the appropriate inner temperature. This protects against undercooking and overcooking, ensuring food safety and desired doneness.
2. Kinds Of Meat Thermometers
- Dial Thermometers: Include a steel probe with a dial for reviewing temperatures. Place the probe into the thickest part of the meat.
- Digital Thermometers: Offer fast and precise readings with a digital screen. Perfect for accurate temperature measurement.
- Instant-Read Thermometers: Deal fast results, normally within a few secs. Perfect for checking temperature level during food preparation.
3. Just how to Use a Meat Thermometer
- Put Correctly: Put the thermostat into the thickest part of the meat, avoiding bones and fat.
- Check Temperature Level: Guarantee the meat gets to the advised inner temperature for security and top quality.
- Clean After Use: Laundry the probe with hot, soapy water before and after usage to prevent cross-contamination.
4. Recommended Inner Temperatures
- Chicken: 165 ° F( 74 ° C).
- Beef, Pork, Lamb: 145 ° F( 63 ° C).
- Ground Meats: 160 ° F (71 ° C).
- Fish: 145 ° F (63 ° C).
Checking Doneness.
1. Visual Cues
- Meat Color: For several meats, a modification in color shows doneness. As an example, fowl should no more be pink, and beef needs to have a clear, reddish-pink color for medium-rare.
- Juices: Clear juices usually represent that meat is cooked via, while pink or red juices could show that extra cooking is needed.
2. Tactile Cues.
- Texture: Firmness can be a excellent sign of doneness. For instance, a well-done steak will certainly feel firm, whereas a unusual steak will feel soft.
- Touch Examination: Contrast the suppleness of the meat to the suppleness of the hand of your hand for a harsh scale of doneness.
3. Food Preparation Times and Doneness.
- Follow Recipes: Dishes offer cooking times based on certain temperatures and meat cuts. Readjust these times based on your specific oven or altitude.
- Resting Time: Allow meats to rest after food preparation. This helps redistribute juices and can impact last texture and temperature level. Relaxing times can differ yet normally range from 5 to 15 minutes depending upon the size and kind of meat.
4. Oven Tracking.
- Use a Timer: Establish a timer based upon the recommended food preparation time. Check your food periodically as stoves vary.
- Adjust as Needed: If utilizing a convection oven or cooking at high elevations, keep in mind to change the cooking time and temperature level as required.
Typical Blunders and Exactly How to Prevent Them.
- Overcooking: To avoid overcooking, monitor your food very closely and utilize timers. Bear in mind that some foods continue to cook after being gotten rid of from heat.
- Undercooking: Undercooking can be avoided by complying with suggested times and inspecting doneness with a thermostat or other approaches.
Changing Cooking Times for Recipes.
- Modifying Times for Different Sizes: Readjust cooking times based on the dimension of your food. Bigger pieces take longer, while smaller items prepare much faster.
- Adapting for Personal Preferences: Personal taste can influence cooking times. For instance, if you favor well-done meat, cook a bit longer than the standard time.
Verdict.
Understanding just how to utilize a cooking time graph is a important ability in the kitchen. It aids guarantee that your dishes are cooked to excellence, balancing security with taste and structure. By comprehending the essentials of cooking times and how they vary by food kind and approach, you can boost your cooking performance and avoid usual errors. Remember, food preparation is as much regarding experience as it has to do with guidelines, so make use of these charts as a starting factor and adjust as required to fit your choices and cooking area conditions.
Frequently Asked Questions.
- Exactly how do I readjust cooking times for frozen foods?
- Frozen foods generally need extra cooking time. Check the package guidelines for details recommendations.
- What’s the very best method to guarantee even cooking?
- Ensure even cooking by using consistent sizes for your food and turning or stirring it as needed.
- Can I make use of the very same cooking time chart for all ovens?
- While graphes offer basic guidelines, individual stove efficiency can vary. Use an stove thermometer for finest outcomes.
- Just how do I transform cooking times for various food preparation approaches?
- Different techniques can influence cooking times. For example, baking might require even more time than steaming. Usage particular charts for every approach or adjust based on experience.
- What should I do if I don’t have a cooking time graph?
- In the lack of a chart, describe dish standards, and readjust based on the size and kind of food. Utilize a thermostat to make certain proper doneness.