Spiral Ham Cooking Time Chart With Glaze – Cooking is both an art and a scientific research, and recognizing the ideal cooking times can make all the distinction between a delicious meal and a culinary disaster. Whether you’re a experienced cook or a home cook, having a reputable food preparation time graph available is vital. In this short article, we’ll dive deep into the world of cooking times, breaking down every little thing you require to know to ensure your dishes turn out perfectly every time. Spiral Ham Cooking Time Chart With Glaze.
Significance of Knowing Cooking Times
Food preparation times are crucial for making sure that your food is cooked extensively and securely. Correct cooking not just enhances the taste and appearance of your dishes yet also helps prevent foodborne ailments. Overcooking or undercooking can dramatically influence the high quality of your meal, making understanding food preparation times a essential skill in the kitchen area.
How Cooking Times Affect Food Top Quality
Cooking times can impact greater than just security; they additionally influence taste and texture. For instance, overcooked meat can become challenging and dry, while undercooked fowl can be risky to eat. A cooking time graph assists you strike the appropriate equilibrium, ensuring your recipes are both secure and delicious.
Comprehending Cooking Times
What are Cooking Times?
Cooking times describe the duration needed to prepare food to the desired doneness degree. These times can differ based upon the type of food, its size, and the cooking approach used. A well-structured food preparation time graph provides a quick recommendation for these times, making dish preparation extra efficient.
Elements Affecting Food Preparation Times
Several elements can influence cooking times, including:
- Dimension and Thickness: Larger or thicker items of food typically require even more time to cook.
- Cooking Approach: Various approaches (e.g., baking, grilling) can impact exactly how promptly food chefs.
- Temperature: Cooking at greater or reduced temperatures will alter cooking times.
- Elevation: Food preparation times can be much longer at greater altitudes due to lower atmospheric pressure.
Food Preparation Time Graph Basics
Types of Cooking Time Charts
Cooking time graphes can be classified right into numerous types:
- General Charts: Offer ordinary cooking times for numerous foods.
- Specialized Charts: Focus on particular classifications like meats or veggies.
- Method-Specific Graphes: Information times based on cooking techniques like cooking or barbecuing.
How to Make Use Of a Food Preparation Time Graph
Making use of a cooking time graph is easy. Discover the type of food and its preparation technique, then refer to the recommended time. Readjust based upon your particular conditions, such as stove kind or food size.
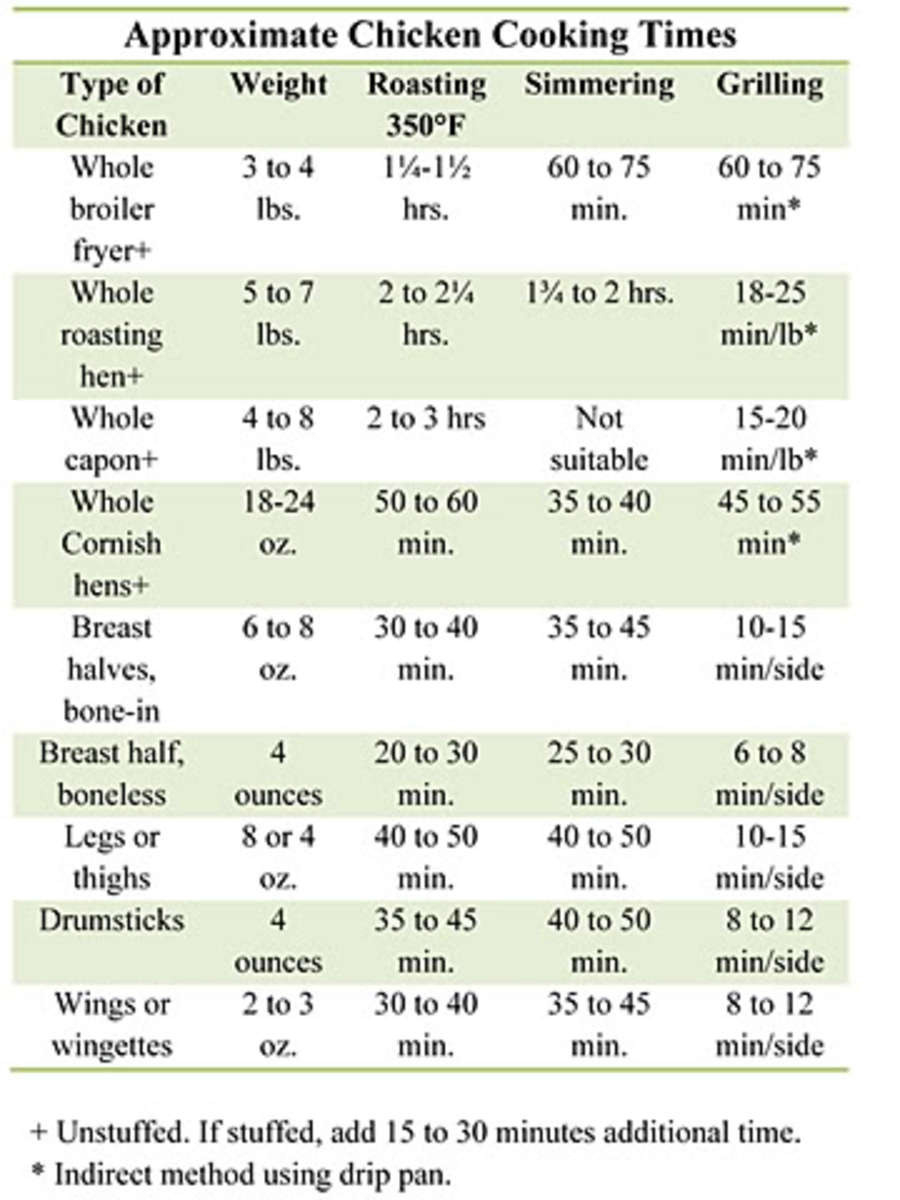
Meat Cooking Times
Beef
- Roasts: For a medium-rare roast, cook at 325 ° F( 163 ° C) for about 20 minutes per pound.
- Steaks: Grill or pan-fry for regarding 4-5 minutes per side for medium-rare.
Pork
- Roasts: Prepare at 325 ° F( 163 ° C) for 25 minutes per pound.
- Chops: Grill or pan-fry for 6-8 minutes per side, depending on thickness.
Poultry
- Whole Chicken: Roast at 350 ° F( 177 ° C )for about 20 mins per pound.
- Chicken Breasts: Cook at 375 ° F( 190 ° C) for 25-30 mins.
Lamb
- Roasts: Cook at 325 ° F( 163 ° C )for about 25 mins per pound for medium-rare.
- Chops: Grill or pan-fry for 4-5 mins per side.
Seafood Cooking Times
Fish
- Whole Fish: Cook at 400 ° F( 204 ° C) for 20 mins per
- pound. Fillets: Cook at 375 ° F( 190 ° C )for 15-20 mins.
Shellfish
- Shrimp: Boil or sauté for 3-4 minutes up until pink and opaque.
- Lobster: Steam for regarding 7-10 minutes per pound.
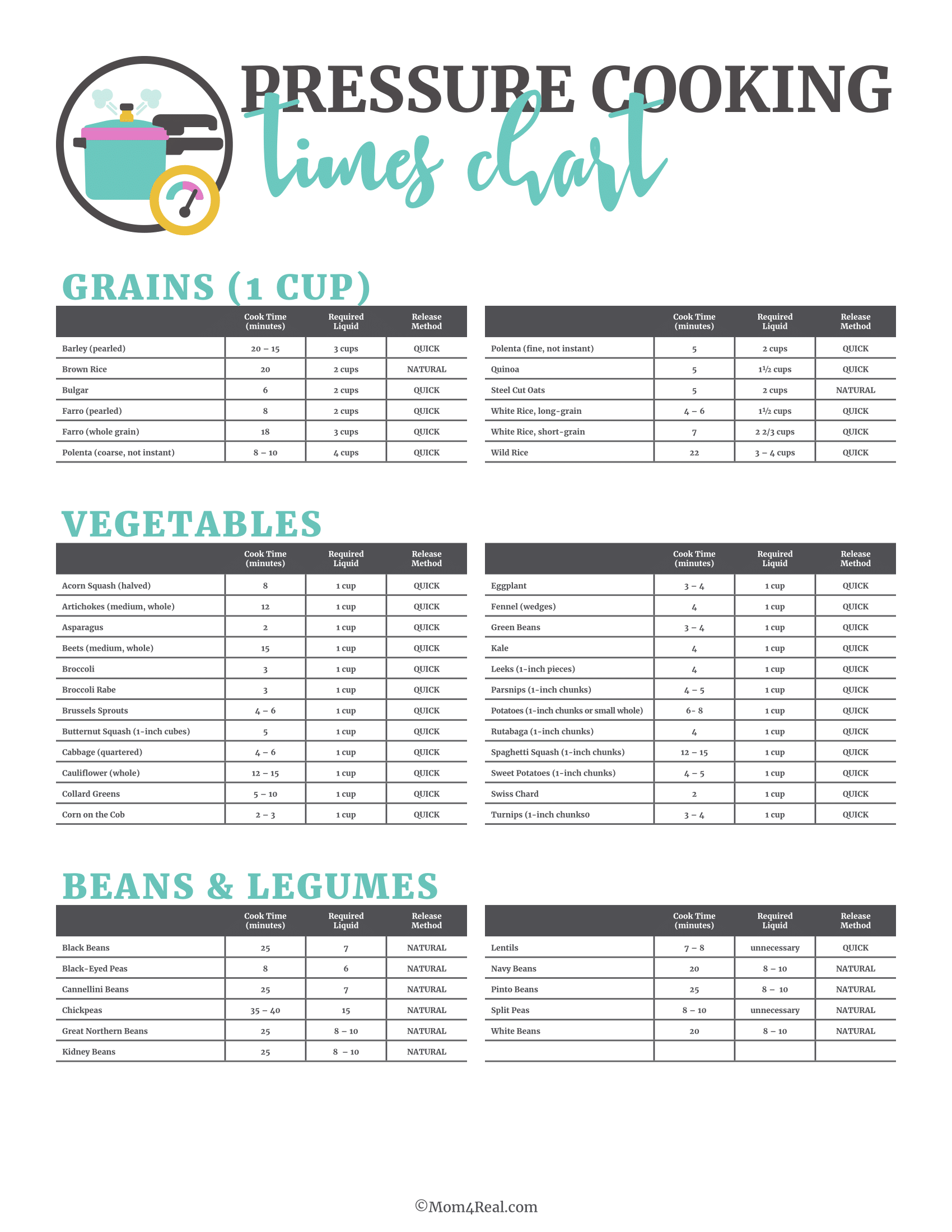
Veggie Food Preparation Times
Origin Veggies
- Potatoes: Bake at 400 ° F( 204 ° C )for 45-60 minutes, depending upon dimension.
- Carrots: Boil for 5-7 mins or roast for 25-30 minutes.
Leafy Greens
- Spinach: Sauté for 2-3 mins until wilted.
- Kale: Sauté or cook for 10-15 minutes.
Cruciferous Vegetables
- Broccoli: Heavy steam for 5-7 minutes.
- Cauliflower: Roast at 425 ° F( 218 ° C )for 20-25 mins.
Food Preparation Times for Different Methods
- Baking: Cooking times vary based upon the meal. Cakes, casseroles, and bread each have unique times and temperatures.
- Boiling: Boiling times depend upon the food. For pasta, it’s usually 8-12 mins; for eggs, concerning 10 minutes for hard-boiled.
- Steaming: Steaming maintains nutrients better. Vegetables usually take 5-10 mins, relying on size.
- Sautéing: Sautéing is quick, generally taking 5-10 mins for vegetables and 3-4 minutes for healthy proteins.
- Grilling: Grilling times vary widely. For meats, it can vary from 4 minutes per side for thin cuts to 20 minutes per side for thicker pieces.
Unique Factors to consider
Altitude and Food Preparation Times
1. Comprehending Altitude Impacts
At greater elevations, the reduced air pressure can impact cooking times and temperature levels. As an example, water boils at a reduced temperature level, which implies that food preparation procedures might require even more time to complete. Readjusting your recipes for altitude can ensure much better results.
2. Readjusting Cooking Times
- Up to 3,000 Feet: Slight adjustments are usually adequate. Boost food preparation time by concerning 5-10% or add a few additional mins.
- 3,000 to 6,000 Feet: Modest changes may be needed. Increase food preparation time by 10-20%, and often increase the temperature level by 25 ° F to ensure correct food preparation.
- Over 6,000 Feet: Substantial adjustments are required. Increase cooking time by 20-30% and adjust temperature level settings as needed. For cooking, you could also need to readjust the amount of fluid and leavening representatives.
3. Baking at High Altitudes
Cooking can be specifically complicated. For cakes and cookies:
- Lower Baking Powder/Soda: Too much can trigger fast climbing and collapse.
- Boost Flour: To make up for the reduced thickness of air.
- Boost Liquid: To combat the quicker dissipation rates.
Oven Variations
1. Stove Temperature Level Precision
Not all stoves heat evenly. A conventional stove could have temperature level variations of up to 50 ° F. This discrepancy can impact food preparation and baking end results.
2. Testing Oven Temperature
To ensure your oven is at the right temperature:
- Make Use Of an Stove Thermostat: Put it in the facility of the stove and compare the reading to your stove’s temperature setting.
- Normal Calibration: Calibrate your stove occasionally to preserve precision.
3. Checking Cooking Times
- Check Early: Start inspecting your food a couple of mins before the advised cooking time to avoid overcooking.
- Changing Recipes: If you discover your oven chefs faster or slower, readjust your recipes accordingly by either lowering or enhancing cooking times.
4. Convection Ovens
Stove distribute air, which can lead to faster and extra even cooking. Generally, reduce cooking time by about 25% or lower the temperature level by 25 ° F contrasted to traditional ovens.
Tips for Accurate Food Preparation Times
Making Use Of a Meat Thermostat
1. Significance of a Meat Thermometer
A meat thermometer is an crucial tool for guaranteeing that meats get to the correct internal temperature. This stops undercooking and overcooking, making certain food safety and security and desired doneness.
2. Types of Meat Thermometers
- Dial Thermostats: Include a steel probe with a dial for reading temperatures. Put the probe into the thickest part of the meat.
- Digital Thermometers: Offer fast and precise readings with a digital display. Ideal for exact temperature dimension.
- Instant-Read Thermometers: Offer fast results, generally within a couple of seconds. Perfect for examining temperature throughout cooking.
3. How to Use a Meat Thermostat
- Insert Correctly: Place the thermometer into the thickest part of the meat, preventing bones and fat.
- Examine Temperature: Guarantee the meat reaches the advised internal temperature level for safety and top quality.
- Tidy After Usage: Clean the probe with warm, soapy water before and after use to stop cross-contamination.
4. Recommended Internal Temperature Levels
- Fowl: 165 ° F( 74 ° C).
- Beef, Pork, Lamb: 145 ° F( 63 ° C).
- Ground Meats: 160 ° F (71 ° C).
- Fish: 145 ° F (63 ° C).
Inspecting Doneness.
1. Aesthetic Hints
- Meat Shade: For several meats, a adjustment in color suggests doneness. For example, chicken must no more be pink, and beef needs to have a clear, reddish-pink shade for medium-rare.
- Juices: Clear juices typically signify that meat is prepared through, while pink or red juices may indicate that additional cooking is required.
2. Responsive Cues.
- Texture: Suppleness can be a great indication of doneness. As an example, a well-done steak will certainly really feel strong, whereas a uncommon steak will really feel soft.
- Touch Examination: Compare the suppleness of the meat to the suppleness of the palm of your hand for a rough gauge of doneness.
3. Cooking Times and Doneness.
- Adhere To Recipes: Recipes supply cooking times based upon specific temperatures and meat cuts. Change these times based upon your specific stove or altitude.
- Relaxing Time: Enable meats to relax after cooking. This aids redistribute juices and can impact last structure and temperature. Relaxing times can differ yet usually array from 5 to 15 minutes depending on the size and kind of meat.
4. Oven Surveillance.
- Use a Timer: Set a timer based on the advised food preparation time. Examine your food regularly as ovens vary.
- Change as Needed: If making use of a stove or food preparation at high altitudes, remember to change the cooking time and temperature level as required.
Common Mistakes and How to Stay clear of Them.
- Overcooking: To avoid overcooking, check your food very closely and use timers. Bear in mind that some foods remain to prepare after being eliminated from heat.
- Undercooking: Undercooking can be avoided by adhering to recommended times and inspecting doneness with a thermometer or various other techniques.
Readjusting Food Preparation Times for Recipes.
- Changing Times for Various Dimensions: Adjust cooking times based on the dimension of your food. Bigger items take longer, while smaller pieces cook faster.
- Adapting for Personal Preferences: Personal taste can affect cooking times. For instance, if you favor well-done meat, prepare a bit longer than the standard time.
Verdict.
Understanding exactly how to use a cooking time graph is a beneficial skill in the cooking area. It assists make certain that your meals are prepared to perfection, balancing security with taste and texture. By comprehending the fundamentals of cooking times and just how they differ by food kind and approach, you can improve your cooking efficiency and avoid common errors. Keep in mind, cooking is as much concerning experience as it has to do with standards, so utilize these charts as a beginning point and adjust as required to fit your preferences and cooking area problems.
Frequently Asked Questions.
- How do I readjust cooking times for frozen foods?
- Frozen foods generally call for additional cooking time. Inspect the package guidelines for particular recommendations.
- What’s the best method to make certain even cooking?
- Guarantee also cooking by using consistent sizes for your food and turning or stirring it as required.
- Can I use the very same food preparation time chart for all ovens?
- While charts provide general guidelines, private oven performance can vary. Use an stove thermometer for ideal outcomes.
- Just how do I transform cooking times for various cooking methods?
- Different techniques can impact cooking times. As an example, baking might need more time than steaming. Use specific charts for each and every method or change based on experience.
- What should I do if I don’t have a cooking time graph?
- In the lack of a graph, refer to dish guidelines, and readjust based on the size and kind of food. Use a thermostat to ensure appropriate doneness.